OpenAI Aardvark is a major step toward fully autonomous cybersecurity. Built on GPT-5, Aardvark is an intelligent agent that can read, understand, and repair software code with human-like precision. Instead of just scanning for known vulnerabilities, it actively reasons about how code works, detects potential flaws, validates whether they can actually be exploited, and then produces its own patch to fix them.
OpenAI describes Aardvark as an agentic security researcher. It operates continuously within a development environment, reading repositories, monitoring commits, and identifying weak points before attackers can exploit them. Unlike traditional scanners that rely on static patterns, Aardvark uses deep reasoning and contextual understanding to find problems that conventional tools often miss.
Table of Contents
- What is Aardvark
- How Aardvark Works
- Inside GPT-5 and Aardvark
- Early Results and Private Beta
- How Aardvark Differs from Other Tools
- Integration and Workflow
- Open Source and Responsible Disclosure
- Why Aardvark Matters for the Future of Software Security
What is Aardvark
Aardvark is a continuous security companion that acts as a researcher embedded directly into a codebase. It is capable of monitoring software as it changes, discovering vulnerabilities as they appear, and generating contextual explanations and patches. This approach allows Aardvark to assist developers in real time, reducing the window between vulnerability discovery and mitigation.
While traditional vulnerability scanners or static analyzers depend on predefined rules, Aardvark relies on GPT-5’s reasoning abilities. It understands how code behaves in practice, not just what it looks like on the surface. This enables it to spot logic flaws, unsafe configurations, and incomplete patches that would normally require an experienced human auditor to catch.
How Aardvark Works
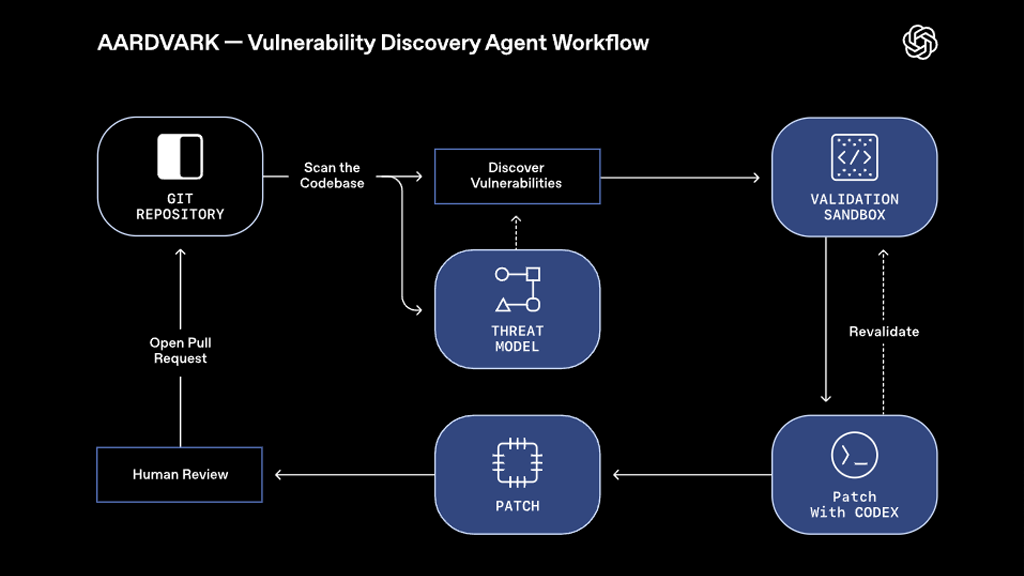
Aardvark’s workflow resembles the daily routine of a real security researcher, but it operates continuously and at scale. It connects to repositories such as GitHub and performs the following tasks:
- Code analysis: Aardvark begins by analyzing the full repository to form a high-level understanding of how the system is structured and what its security goals are. It builds a mental model of how components interact.
- Threat modeling: Using this understanding, it constructs an internal threat model that predicts potential attack vectors, unsafe input points, and privilege boundaries.
- Commit scanning: It inspects both historical and new commits for risky changes. Every new update is analyzed against the project’s threat model to detect regressions or new vulnerabilities.
- Exploit testing: When a potential flaw is detected, Aardvark attempts to reproduce it safely in a sandbox. This step eliminates many false positives because it verifies that an issue can actually be exploited.
- Patch creation: Once confirmed, Aardvark uses OpenAI’s Codex system to generate a secure patch. It writes an explanation, produces a pull request-ready fix, and attaches its reasoning so that human engineers can review it easily.
By combining reasoning, real exploit testing, and automated patching, Aardvark offers developers something unique: verified findings that come with immediate, context-aware solutions.
Inside GPT-5 and Aardvark
GPT-5, the model that powers Aardvark, is OpenAI’s most advanced reasoning system to date. It uses improved architecture, long-context understanding, and better tool-use orchestration. Aardvark leverages GPT-5’s ability to break down complex programming logic and to make decisions about when to use external tools like sandboxes, compilers, or debuggers.
GPT-5 also introduced the concept of a “real-time router.” This means that Aardvark can dynamically decide how to analyze code based on its complexity or risk level. It can use lightweight reasoning for simple checks or full in-depth analysis when handling core security modules.
This layered reasoning capability allows Aardvark to act like multiple experts in one: part penetration tester, part code auditor, and part developer assistant. It doesn’t just detect problems—it understands their consequences and proposes practical solutions.
Early Results and Private Beta
OpenAI has been using Aardvark internally across its own codebases and among a select group of external partners. According to OpenAI, Aardvark has already identified at least ten unique vulnerabilities in open-source software that have been assigned official CVE numbers.
In benchmark testing, Aardvark successfully detected 92 percent of known and synthetic vulnerabilities introduced into “golden” test repositories. It also demonstrated a low false positive rate by validating exploits through live sandbox testing before reporting them.
Developers who have tested Aardvark in early access noted that it uncovered subtle bugs such as logic errors, incomplete mitigations, and misconfigured permissions—issues that typical scanners fail to detect.
How Aardvark Differs from Other Tools
Aardvark is not just another vulnerability scanner. It represents a fundamental change in how security automation works. Most traditional tools depend on signature databases, pattern matching, or syntax analysis. Aardvark, on the other hand, uses contextual understanding and critical reasoning to evaluate risk in the same way a human would.
Its ability to test potential vulnerabilities in isolation sets it apart. Instead of flagging every possible issue, Aardvark focuses on those that are provably exploitable, saving developers time and reducing alert fatigue. The addition of automatic patch generation makes it both a detection and remediation engine in one workflow.
Integration and Workflow
Aardvark integrates with existing DevSecOps pipelines, especially through GitHub Cloud. It monitors repositories continuously and adds findings directly into pull requests. Each report includes annotated code, a detailed explanation of the vulnerability, and a Codex-generated patch that can be reviewed and merged by the engineering team.
- Seamless integration with existing CI/CD tools.
- Support for multiple languages and frameworks.
- Reports formatted for human review, not just machine output.
- No training on user code during the private beta.
OpenAI has stated that Aardvark is designed to assist, not replace, developers and security professionals. It acts as a real-time teammate that reviews every commit with a security-focused perspective, augmenting human expertise rather than automating it blindly.
Open Source and Responsible Disclosure
Beyond private deployments, OpenAI has used Aardvark to help secure the open-source ecosystem. The company has responsibly disclosed vulnerabilities found by the agent and has committed to offering free scanning for select non-commercial open-source projects.
OpenAI also updated its coordinated disclosure policy to encourage collaboration rather than pressure. By allowing maintainers to work directly with Aardvark’s findings, the process of patching open-source vulnerabilities becomes more transparent and efficient.
Why Aardvark Matters for the Future of Software Security
Every year, tens of thousands of new software vulnerabilities are discovered, and many go unpatched for months. Aardvark represents a new approach that shifts security left—catching flaws as soon as they are introduced. By continuously learning and reasoning about software systems, Aardvark could redefine how organizations think about secure development.
As the complexity of modern codebases continues to grow, tools that combine intelligence, automation, and verification will be essential. Aardvark bridges the gap between AI research and applied cybersecurity, showing how large language models like GPT-5 can directly improve digital safety.
With future versions expected to expand to on-premise repositories and enterprise integrations, Aardvark could soon become a core part of how developers secure their software. It is not just a product demonstration—it is the beginning of a new phase in AI-driven code defense.
Learn More
- Official OpenAI Aardvark Announcement
- Apply for Aardvark Private Beta
- Learn About GPT-5
- Explore Cybersecurity Insights
OpenAI Aardvark combines artificial intelligence, automation, and human reasoning into a single tool that strengthens code security without slowing innovation. As the software world faces an ever-expanding threat landscape, Aardvark stands as one of the most ambitious attempts yet to make secure development the default rather than the exception.



Leave a Comment